From the moment we first meet with patients,
we will take care of them like a family with faith, hope, and love.
Wellness Hospital treats even the hearts of customers through experts treatment and specialized medical services.
1
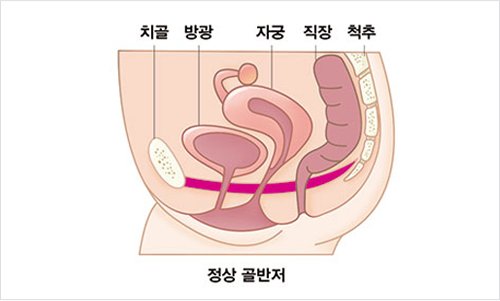
What is the pelvic floor?
The pelvic floor normally supports and protects the urinary organs (bladder, urethra), reproductive organs (uterus, vagina), and intestines (small intestine, large intestine) located in the pelvis. This will help you urinate and feces better and keep your sex life healthy.
2
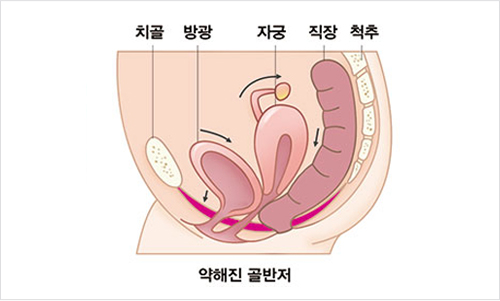
What are pelvic floor disorders?
When there is an anatomical, functional, or physiological problem in the organs of the pelvic floor, it is called pelvic floor disorder, and disorders such as urinary storage and urination disorders, pelvic organ prolapse, and sexual dysfunction belong to this category. Anatomically, the pelvis is made up of bones and the bottom part is made up of various muscles and ligaments. The muscles and ligaments that make up the pelvic floor are under pressure to support all the abdominal organs. Especially in the of women, while supporting the weight of the baby and amniotic fluid, which weighs approximately 10 kg in the second half of pregnancy, the muscles are stretched during the period. Pelvic floor disorder is a disease that occurs when these weakened muscles gradually sag.
-
1
More than 80% of all patients are women.
-
2
The main causes are aging, pregnancy, childbirth and trauma.
-
-
-
5
Congenital diseases and mental disorders
Low-tone Pelvic Floor Disease
A condition in which the pelvic floor muscles are atrophied or weakened, making it impossible to contract the pelvic floor muscles, resulting in pelvic floor dystonia, pelvic organ prolapse, rectal flow, fecal incontinence, and stress incontinence.
4
Classification of pelvic floor disorders
A convex protrusion of the weakened rectal wall toward the vagina is called a protocele. Because the wall between the rectum and vagina is relatively thin and weak in women, constipation is usually severe. If you are constipated so badly that you repeatedly force yourself to pass a bowel movement, the wall of the rectum-vaginal stretches like a balloon, resulting in a proctocele.
If the proctocele is severe, you may need to squeeze or dig up the stool with your fingers. In other words, surgery should be performed when part of the stool remains in the proctocele even after defecation.
-
· Examination methods for proctocele
digital rectal examination, anal pressure test, and defecation angiography
-
· Treatment method
Non-surgical treatment :Non-surgical treatment is possible if the size of the rectum is not large. It is important to maintain a healthy bowel habit, eat foods high in fiber, and drink at least 6 to 8 glasses of water per day.
Surgical treatment : Surgery is performed when a portion of the stool remains within the rectum even after defecation, usually when the size of the rectal mass is 3 cm or more on defecation angiography. The surgical method is to pull the stretched muscle on the wall between the rectum and the vagina and sew it tight. Surgery can be done through the anus, the vagina, and the perineum depending on the condition and location of the disorder.
It refers to the condition in which the rectum is inverted through the anus. In advanced rectal prolapse, anal sphincters get damaged and weakened, and they result in symptoms like fecal incontinence, sticky mucus secretion or gas, or inability to hold stool.
At first, a feeling of receding anus during defecation, a feeling of incomplete defecation, pain, a feeling of a foreign body in the rectum, mucus secretion, and diarrhea may occur. Eventually, the anus will come out and it will not go back to the right position.
-
· Diagnosis and Testing
Checking the prolapsed intestine, questionnaire, and defecography.
-
· Treatments
The longer the rectal prolapse remains, the more severe the damage and the more likely it is to cause fecal incontinence. Therefore, you need to see a specialist for surgery as soon as possible. Surgical treatment is the only way to cure rectal prolapse. Laparoscopic ventral mesh rectopexy (LVMR) is a painless and quick recovery procedure. It is a highly difficult operation that is only performed in a few hospitals in Korea, including the Wellness Hospital, but it usually results in a high level of satisfaction from patients. It is a surgery that is mainly performed for rectal prolapse in Europe, and usually involves less pain and reduced recurrence rate.
Fecal incontinence is a symptom in which farts, diarrhea, soft stools, or hard stools come out regardless of one's will. There are cases where the stool comes out even when you cough or fart, and there are times when you feel the need to defecate, but you can not stand it and make a mistake with your clothes.
-
· Diagnosis and Examination
Questionnaire, anal finger test, anal pressure test, and anal ultrasound
-
· Treatments
Non-surgical treatments : Food control, Kegel exercise, Biofeedback
Surgical Treatments : anal sphincter reconstruction, transplantation, plastic surgery, and trans ischiorectal tape (TIRT)
It refers to a phenomenon in which urine is discharged regardless of one's intention. In women, various muscles supporting the bladder or pelvis gradually loosen due to the physiological process of repeated pregnancy and childbirth, resulting in urinary incontinence. These changes become more severe when the female hormones decrease during menopause. Coughing or laughing can make urine leakage worse.
-
· Diagnosis and Examination
urodynamic examination and ultrasound test
-
· Treatment
Non-surgical treatments : Kegel exercises and biofeedback treatment
Surgical Treatments : tape surgery such as TOT surgery
It occurs when the pelvic floor muscles are weak and cannot support the bladder, so the bladder droops like a pocket. In this case, frequent urination, incomplete and insufficient urination, a heavy feeling in the abdomen, and the weak internal mucous membrane protruding outward are severe and painful.
-
· Diagnosis and Examination
urodynamic examination, ultrasound examination
-
· Treatments
Surgical Treatments : Most of the cystoceles require surgical treatments, which involve an incision in the anterior wall of the vagina to push the bladder in and pull the muscles to strengthen them.
High-tone pelvic floor disease
It refers to a state in which the pelvic floor muscles are overly tense and result in spastic paralysis, increasing the inability to contract and relax the pelvic muscles. Symptoms include dysuria, frequent urination, urgent urination (overactive bladder and painful bladder syndromes), pelvic pain, and dyspareunia.
Pelvic Floor Dyssynergia
This is a phenomenon seen in patients with chronic constipation, which means that the pelvic floor muscles and anal muscles, which are supposed to relax and open the anus during defecation, fail to contract appropriately and fail to release stools.
5
Diagnosis and examination of pelvic floor disease
-
· Diagnosis and Examination
clinical questionnaire and examination, defecation angiography, intraanal pressure test, urodynamic examination, ultrasound examination, CT, etc.
-
· Treatments
Non-surgical treatments :pelvic muscle exercise (Kegel exercise), biofeedback, and electrical stimulation therapy.
Surgical Treatments : If there is no improvement with these non-surgical treatments, surgery should be performed for each disease.